When launching a new website, there are some things that seem unimportant at first, but turn out to really be an issue later on. One of them is the WWW vs. Non-WWW issue.
When you first think about it, it doesn’t sound like much of a deal. You might not even care at all about it. When you first research it, you’ll probably learn around the web that it doesn’t really matter for SEO.

However, if you start digging deeper, you’ll discover a lot of things you didn’t know. So did I, so follow this journey to understand once and for all why this hassle about which one is better.
- Short History of the WWW
- Pros & Cons of WWW and Non-WWW
- Does It Matter for SEO?
- What Should YOU Choose
While the truth is that it doesn’t directly matter whether your domain is WWW or Non-WWW for SEO, it can impact it very slightly. That’s because it can potentially impact performance (although in a very slight way) and performance impacts UX, which ultimately impacts SEO.
Short History of the WWW
There’s something about the WWW that you probably haven’t thought of. The fact that it’s actually a subdomain. However, because it has become so popular, people almost forgot that.
You see, the World Wide Web (www) isn’t the only thing on the internet. You also have mail, smtp, pop, ftp and other important functions that are all run under specific subdomains.
Back in the day when the internet was not so popular and e-mail was the actual thing, a web server would have the domain name alias of WWW assigned to it, just like any other protocol.
Over time, the web became the most popular thing on the internet. (Google also kind of took control of it).

People would type the URLs manually, often excluding the WWW. Webmasters caught on to this and started using the Non-WWW domain as the preferred variant.
This could be an issue for webmasters as Google sees http://www.example.com and http://example.com as two separate entities, therefore creating duplicate content issues. However, most websites now correctly 301 redirect the unused version to the preferred one. You should also note that through 301s, some of the link equity could get lost, so it’s always better if you get all your backlinks pointing to the preferred version.
Pros & Cons of WWW and Non-WWW
Both the WWW and Non-WWW versions have their upsides and downsides. Let’s outline them so that you can quickly decide which one you think is best.
Interestingly, there are 2 websites dedicated to this issue, which I will list soon enough.
WWW Pros and Cons
WWW has been the standard for many, many years. Many people still associate www with websites.
However, these are not the pros. Not by far. You see, because of how the web works, WWW allows you to do some really cool things.
First, it allows you to set some cookies only for that particular www subdomain. Cookies get passed in a hierarchical way. This means that if you set a cookie for www.domain.com it will be passed to thing.www.domain.com and another.thing.www.domain.com and so on. You’ve guessed it: if you set a cookie for domain.com, it gets passed to all the subdomains.
Usually, the domain level cookies are important ones which you would use anyway, like session IDs and tracking scripts. However, if you want to host your images on a subdomain to remove unnecessary cookies, you won’t be able to do so by setting a cookie to the root domain.
Using WWW ensures that you only send the cookies to the WWW version, leaving any other subdomains, such as static.domain.com or img.domain.com cookie-free.
Secondly, a subdomain is more flexible, at least DNS-wise. That means you’ll be able to use CDNs (Content Delivery Networks) a lot easier.
As cons, we could say that WWW is kind of ancient. Eventually, the web will probably adapt to using the non-WWW with full potential, but it might take a while. I mean, who knows, maybe at some point we won’t even use URLs anymore.
But for now, the technology is still relying on old protocols and www is not likely to go away very soon due to its vast and efficient uses.
You can read more about the pros of using www on https://www.yes-www.org.
Non-WWW Pros and Cons
If you don’t use WWW, you get a prettier and shorter domain. Shorter domains have been associated with higher rankings, but that could only be a correlation.
Also, if you won’t use any cookies or if your cookies are anyway required everywhere (including images), then you will save bandwidth as there are 4 more bytes of data to be sent (www are 3 and the 4th is the dot before your domain name).
You could also say that the domain is easier to remember, spell, type and tell. This isn’t an issue with direct traffic, as there are 301s that always take the user to the good version, but it can leak link juice through the redirects. Ideally, all the backlinks should go to only one version instead of being always slip into two. This applies regardless of whether you use WWW or not.
The cons are basically the opposite of what the pros are for the WWW version:
Firstly, you can’t restrict root cookies only to the root domain, as they will always get passed on to all subdomains. However, most blogs and websites host images on the same domain anyway so the cookies get sent either way.
Secondly, it will be harder to get a CDN to work, as you will not be able to set a CNAME record for your root/naked domain without messing up other things like FTP and Mail.
Apparently, using a non-www version can also be less secure, however this is only applicable if you don’t use HTTPS and secure cookies.
If you want to see the pros of a non-www web page, go to https://dropwww.com/why.
As you can see, the reasons to drop WWW are a little more puerile. They don’t get into the technical issues at all. It seems like the reasons to keep WWW are rather stronger.
Don’t rush to decide. Not yet! Read the next section and you’ll understand why.
So which one is better?
“Ok, from what I can tell it seems like we’re better off using the WWW. It spares us of all the hassle.“
True. As a matter of fact, I can’t really think of a big website that doesn’t use WWW.
Well, there are workarounds.
Although WWW seems like the best option, there are workarounds that make Non-WWW just as good.
We all like workarounds, especially when we really, really want to get to that result, don’t we? If you’re set in your head that you really want to go for the naked domain, then don’t worry. There are ways.
First, you could use a completely separate domain for hosting your static content. Yahoo mentions this in its guidelines. For example, they use yimg.com to host their static content.
The downside is, obviously, that you have to pay $8.99 per year for another domain. Not really a downside.
Also, if you really want to go for a CDN without using WWW, it’s possible. There are CDNs out there that have found workarounds by using some techniques called CNAME Flattening, ANAME or alias records.
You can read more about these techniques here.
Cloudflare, for example, uses CNAME Flattening and it is a perfectly viable option to use CDNs without WWW in your domain.
Considering all the workarounds available these days, choosing between www and non-www is more and more a matter of preference.
Does it matter for SEO?
In short, (directly) no. From an SEO perspective it doesn’t make a difference whether you use WWW or not in front of your domain name. What’s important is that you have a preferred version and redirect all others to that one.
Make sure that you take all the versions into account. If you also consider things like HTTPS and /index.php, you get around 8 possible combinations that should all be pointing to a single location.
Google’s officials kind of said the same thing. However, the answer is very nuanced:
Minimal SEO implications, IMO. It’s a brand decision, in part, and audience (-savvy) decision, in part. On a new site, shouldn’t impact SEO.
— Dr. Pete Meyers (@dr_pete) August 3, 2017
Minimal implications doesn’t really mean NO implications. Yadayada what? So on an older site it could impact SEO?
Well… If you think about it… there are some things that could slightly influence the SEO on the long run, mainly related to performance. As you know, Google really takes User Experience into consideration when it comes to ranking website. And users very much like speed. So the faster a site is, the better it will usually rank. Both CDNs and Cookie-less static resource loading are speed related improvements.
For smaller websites, it doesn’t really matter. As explained above, there are two main reasons why WWW still stands out:
- You can set static.yourdomain.com as your cookie-less static resource loader. This will slightly improve the speed of your site. However, quantified with thousands of images and billions of hits and requests, it does add up quite substantially.
- You can add a CNAME record without any issues, therefore making it easier to connect to CDNs and distribute your content faster around the Globe.
However, if you’re only targeting your local market, CDN’s don’t really make a difference. If you have a small site, you probably don’t have a ton of images and also not very many cookies.
In the end, it’s pretty much a matter of speed.
With today’s servers and internet connections, a couple of cookies won’t make a difference in speed but it can make a difference in price depending on your bandwidth limits. It adds up over time, you know?
If they were to be compared, the speed is pretty much the same in many cases. Take a look at this comparison between our site and our competitor Moz. Although they also run without WWW, they host their images on a separate, cookie-less domain and distribute static content such as images and scripts through a CDN.
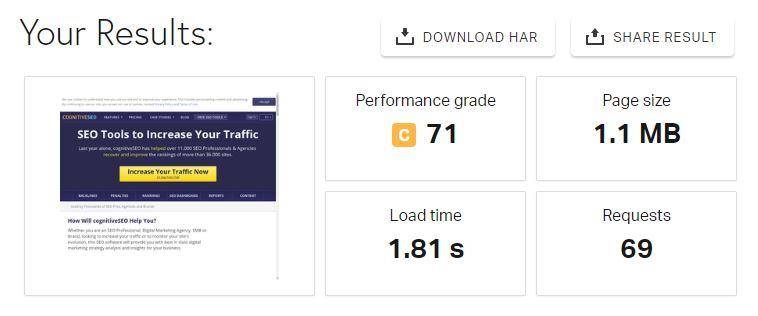
cognitiveSEO results
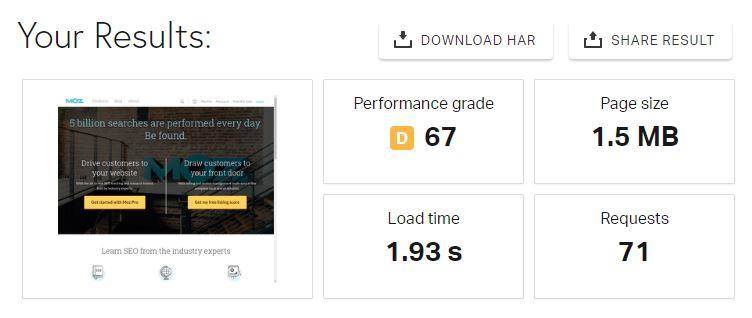
Moz results
They use a CDN which hosts their images on a cookie-less domain. The results? Not very different from us. We don’t use a CDN and don’t host our images on a cookie-less domain.
What Should You Choose
The answer is pretty simple. If you’re a blogger and don’t plan on becoming the biggest site in the world, it doesn’t really matter. Just go with whatever you like. If you really like the www version, feel free to choose it. You’ll get the benefit of having shorter and prettier URLs, which is always good for starters.
If you’ll ever need to go CDN or cookie-less for static resources, you can just use the workarounds. They aren’t any more complicated and also not a big expense.
However, if you’re planning on launching a very big website with potentially thousands of images and a lot of traffic, then it’s probably better to listen to your developers and go with the WWW version. It will make things a lot easier in the long run.
Remember: if you’ve already set the preferred version and Google has indexed it, stick to it! Unless the website has been published 2 days ago and only has 1 page, it’s not worth going through all the hassle and risk your rankings just to switch to www or non-www. Just make sure your 301s are in order and keep focusing on the most important things, like publishing and distributing great content.
If you have already published your website and search engines have already indexed it, then stick to the already chosen version!
Conclusion
In the end, it’s pretty clear that WWW is the easier choice if you want to take advantage of easy CDN implementation, more flexible DNS options and limiting cookies to only one place.
However, as the internet evolves, it gets easier and easier to ignore the WWW and host your site directly on the root domain. This makes its URL shorter.
For SEO at least, it’s a matter of preference. I’d say go for the WWW if you don’t really know what you’re doing at all, as it will keep things simple. However, if you really like your domain naked (just like your motorcycles and your women) then know that there are workarounds that can easily solve your problems.
Which version do you prefer? And for those that don’t use the WWW, did you even encounter the issues I’ve mentioned above? Let us know in the comments section, we’re very curious!

 Site Explorer
Site Explorer Keyword tool
Keyword tool Google Algorithm Changes
Google Algorithm Changes

I have been looking for the answer to this question for so long. Finally, todday I am confirmed whether I should use the www or not. Thanks for such nice informative blog
Glad you finally found your answer!
Hello, thanks for the article. I have the following question, if I compare my backlinks with and without www (my 301 go on with www) I have more backlinks on the without version – i dont understand wy- it muss be the same ore the without version less . In your site explorer is the Domain with www -page influence on average and without on low although is redirected.
Very important question: if i’ve always worked with www (most backlinks etc) and still want to switch to without www, is only the set of the 301 enough and don’t lose any power? thanks a lot
Zumer, naturally some equity is theoretically lost through the 301, but it’s negligible.
However, you should consider if it’s really necessary to switch to non-www.
This is a great article. One question I have though is this:
How do you determine which version to set as preferred if a client is ranking both versions incredibly well on a mega site that is getting around 100k views a month?
Do you like at the version with the most traffic?
Rarely have I seen Google not taking this into his own hands, but it’s true that I’ve seen both HTTP and HTTPS so I guess the issue is similar.
As long as the 301s are in place, it shouldn’t really matter. However, I’d go for the version with more high quality backlinks pointing to it.
Recently set up a CDN and found it much simpler without the www. Can still use the naked url in emails and when messaging ppl but probably best to use the www when posting links. Chrome and other browsers now hide the www in the url box so in-browser domains look basically the same, same should hfully happen with link posts going fward
There was a backlash from the community and the WWW should be displayed again.
Depends on what CDN you were using. Also, it’s not best to use WWW or non-www for links, it’s best to use the final version. If you run on WWW, use WWW links, if you run on non WWW use non WWW links.
Considering there are now hundreds of domain extensions like .attorney or .yoga or .whatever, i would definitely use www with those new exotic domains to help visitors understand they’re visiting a website, especially for print (business cards, flyers, ….). Without www people get confused on what it’s about.
Makes a lot of sense 🙂
But I’d still probably be confused if visiting http://www.xxx.xxx xD
great article! thanks for the help but sometimes google also should give this kind of information; sometimes feeling a little lost about this issue
Yeah, Google doesn’t want to share its secrets 🙂
Hi there,
I would like to know if the anchor text on “Yahoo mentions this in its guidelines.” is on purpose or its an error.
And if possible could you really make a guide on how to set up images.mydomain.com for SEO or if you know any guide kindly share with me if possible thanks.
Definitely not on purpose! 🙂 Fixed, you can check the source now.
Normally you would set that subdomain in your cPanel.
So it’s nothing more than setting up a subdomain to work and then uploading the images there.
After you just use the source to display the image on your main website.
A CDN will also be of use.
Thank You Mr. Cojocariu 😀
Just added www. To my domain after a few years. It’s getting a lot more traffic so decided to do it if I get a CDN and because large sites like Verge and Macstories have.
No wondering if it was a good idea as I’m worried I’ll take a hit on seo. I have 301 setup to redirect and told google about the change.
Let’s wait and see I guess :/
Well if you just added it because other sites have it it was a fairly risky move. Take advantage of it and set a cookieless subdomain for hosting images 🙂 Good luck!
I prefer www is best option, if your domain name is small under 8. Non-www is best for long domain names. And both are same in SEO.
Rohit, it seems like you haven’t read the article. I would appreciate it if you do. They’re not the same in SEO.
Hi! If my website is nearly 2years old and uses the non www. If i redirect with 301 to the www version, will my rankings drop?
Hello Mike. If you do the 301 redirects correctly and are 100% sure you don’t mess up, they should not drop. At least that’s what Google says. If they drop, it’s probably going to be insignificant and will recover very soon. However, if you mess up the 301 redirects, yes. They can drop. If you do move from non www to www, make sure you also move now to HTTPS if you don’t have SSL. Better to do one move than two so do them both at the same time.
Your website non-www but your conclusion prefer www. Kinda wierd..
The conclusion is that it depends on what kind of site you have 🙂
It seems to me that the shortest version is better. Without www, the address is more readable and easier to remember. Few of these large websites use the www prefix, so it may be worth not using them.
I had doubts regarding www or non-www for our website. It got pretty clear now.